
We originally printed this story last Easter. We thought it was good enough to share again. Enjoy!
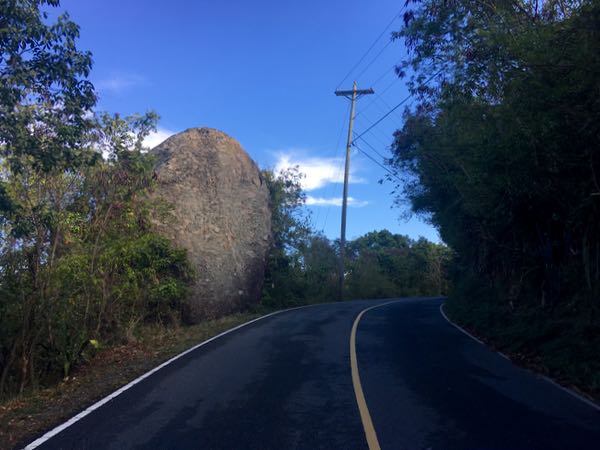
How may of you have driven past the large boulder on North Shore Road between Gibney beach and Peace Hill and wondered what its backstory was? At least a few of you, I’m sure. Well this Easter weekend we’d like to share with you the legend of Easter Rock.
Legend has it that every year on the night before Easter – that’s tonight folks!! – Easter Rock makes its way down to Hawksnest Bay where it takes a drink of water and then rolls back up to its perch on North Shore Road. This all happens before the sun rises over the hill, according to the legend, so no one is around to actually witness it. So even during the driest of droughts, Easter Rock will still be wet on Easter morning.
I’m not sure I’ll be able to make it out to Easter Rock in the morning, but if one of you can on our behalf, I’d love to see some pics. 🙂
So legend aside, curious as to how Easter Rock came to be? Here’s its geological backstory straight from See St. John:
Although geologists have not yet succeeded in explaining Easter Rock’s propensity to go down to the sea on Easter Sunday for a drink of water, they can tell us about the origin of this massive boulder, which is the only one of its kind in the valley.
The outer crust of the Earth consists of large masses of slowly moving rock called tectonic plates. About 100 million years ago, one of these plates, called the North American plate, which was moving towards the west, encountered another tectonic plate called the Caribbean plate, which was moving in the same direction.
Life in the Caribbean has long been classified as slower moving than in the fast-paced world of continental America. This phenomenon apparently has a historical and geological foundation because a significant factor in the creation of many of the Caribbean islands, including St. John, is the fact that the Caribbean plate happened to be moving at a slower pace than its continental counterpart.
Consequently, when the North American plate overtook the slower moving Caribbean plate, the American plate, being denser and heavier, slid under the Caribbean plate and pushed it up. The friction from the two giant masses of solid rock grinding against one another produced a heat so intense that it melted some of the rock between the two plates. The fiery, liquefied rock, called magma, built up in enclosed pockets, called magma chambers, and exerted an ever-increasing pressure on the surrounding rock. When that pressure became so great that it could not be contained any longer, the magma broke through its rocky chamber and spewed forth violently into the ocean. This event is called a volcano.
Normally, when super-hot magma comes in contact with cold ocean water, the magma explodes and is dispersed over a great area. In this case, however, the eruption occurred at a depth of 15,000 feet, or nearly three miles, below the surface of the ocean. At this great depth the water pressure is nearly 7,000 pounds per square inch, a pressure that was sufficient to keep the magma from exploding on contact with water and instead causing it to be deposited on the ocean floor in giant solid sheets.
Coinciding with this volcanic activity and the laying down of rock, the action of the American plate sliding under the Caribbean plate caused the latter to bulge at the edges. The combination of these events resulted in the beginnings of a mountain range that was to become the islands of the Greater Antilles. This process of volcanic activity and uplifting continued for millions of years and caused the newly formed mountains to move closer to the surface.
It was during the next period of St. John’s development that Easter Rock was born. A series of volcanoes erupted in the area of what is today called Pillsbury Sound. This time the water was relatively shallow and the volcanoes erupted explosively. The shower of rocks, solidified volcanic ash, and molten lava added substance and height to the older solid sheets of rock and, in conjunction with the continued uplifting of the area, eventually brought parts of the rocky underwater mass above sea level to form islands.
The awesome power of these violent eruptions also served to break off huge chunks of the older rock, heaving them into the air. One of these massive fragments ended up just above what was to become Hawksnest Bay. That majestic boulder, now known as Easter Rock, not only goes down to the sea every Easter for a drink of water, but also serves as an enduring reminder of the fiery beginnings of the island of St. John.
And there you have it. News you can use today, folks!












































































































Thank you, Jenn, for this geological explanation of how the Caribbean Islands were formed. It is wonderful when you delve into the natural history of the islands, as well as the political and cultural forces that combined to create the land and all its life forms that we love so much today. Well done!
The Jumbies also help the rock on it’s yearly trip and they also help protect Easter Rock. One will also notice the orange cones about 100 yards + away from where the road has started to collapse after Irma, maybe the Jumbies made sure the road collapse was not too close to harm Easter Rock.